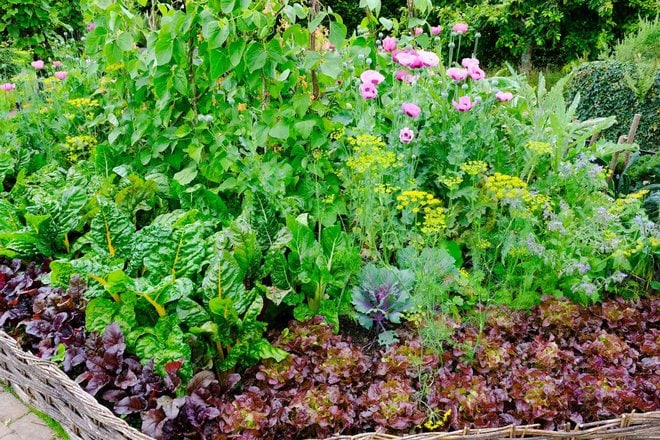
Intensive gardening is a method that allows gardeners to maximize the productivity of limited space by strategic planning and efficient techniques. By utilizing every inch of available area, this gardening approach aims to optimize crop yields and minimize wasted space.
This article explores the concept of intensive gardening and provides tips on how to maximize space in your garden.
The benefits of intensive gardening are numerous. Firstly, it allows individuals with limited garden space to grow a wide variety of crops, ensuring a diverse and nutritious harvest. Secondly, it promotes efficient use of resources such as water, fertilizer, and energy, making it an environmentally sustainable practice. Additionally, intensive gardening can result in higher yields and reduced weed growth, as plants are grown closely together, creating a natural barrier against unwanted vegetation.
To implement intensive gardening successfully, careful planning is essential. This involves designing a garden layout that maximizes space utilization and allows for easy access and maintenance. Choosing the right plants is also crucial, as certain varieties are better suited for intensive cultivation. Furthermore, proper soil preparation, fertilization, watering techniques, and pest and disease management are vital to ensure healthy plant growth and optimal yields.
By following these guidelines, individuals can transform their gardens into productive and efficient spaces, regardless of their size limitations.
Benefits of Intensive Gardening
Intensive gardening offers numerous benefits, including the ability to cultivate a diverse range of crops in a limited space, resulting in a visually vibrant and productive garden that efficiently utilizes every inch of available land.
One of the main advantages of intensive gardening is its ability to maximize space. By using techniques such as raised beds, vertical gardening, and intercropping, gardeners are able to grow more plants in a smaller area. This is particularly advantageous for urban gardeners or those with limited yard space.
Additionally, intensive gardening promotes higher yields and increased productivity. The close planting of crops allows for efficient use of nutrients, water, and sunlight, resulting in healthier and more abundant harvests.
Furthermore, intensive gardening reduces the risk of weed growth and pests, as the dense planting and close proximity of plants create a natural barrier against unwanted intruders.
Overall, intensive gardening is a practical and efficient method for maximizing space and achieving a productive and visually appealing garden.
Plan Your Garden Layout
When planning your garden layout, there are several key points to consider to maximize space and efficiency.
Firstly, utilizing vertical space is a great way to make the most of a small garden. By growing plants vertically, such as using trellises or hanging baskets, you can take advantage of the available height and free up valuable ground space.
Secondly, implementing companion planting can help maximize the productivity of your garden. By planting compatible crops together, you can benefit from their natural synergies, such as pest control or nutrient sharing.
Finally, using raised beds or containers can be a practical solution for limited space. These allow you to have a concentrated growing area, making it easier to manage and maintain your plants.
Utilize Vertical Space
To optimize the use of limited garden space, one effective strategy is to incorporate vertical gardening techniques. By utilizing vertical space, gardeners can maximize their growing area and increase the yield of their crops. Vertical gardening involves growing plants upwards, either on trellises, fences, or walls, instead of spreading them out horizontally. This technique not only saves space but also provides better air circulation and sunlight exposure for the plants.
To make the most of vertical gardening, gardeners can consider using different types of structures, such as vertical planters, hanging baskets, or stacked containers. These structures can be arranged in a variety of ways to suit the available space. Additionally, selecting plants that naturally grow vertically, such as vine crops or climbing flowers, can further enhance the vertical garden.
Below is an example of a 3×3 table that showcases different ways to utilize vertical space in a garden:
| Structure | Advantages | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical planters | Easy to maintain and harvest | Wall-mounted planters |
| Hanging baskets | Adds visual interest to the garden | Suspended planters |
| Stacked containers | Maximizes space and flexibility | Tiered garden containers |
Incorporating vertical gardening techniques is an efficient way to maximize space in a garden. By using structures like vertical planters, hanging baskets, and stacked containers, gardeners can effectively utilize vertical space and grow a variety of plants in a limited area.
Implement Companion Planting
Implementing companion planting in a garden can enhance plant growth and improve overall garden health. Companion planting involves strategically planting different types of plants together to benefit each other in various ways.
Here are three ways in which companion planting can be beneficial:
- Pest control: Certain plants have natural pest-repellent properties, which can help protect neighboring plants from harmful insects. For example, planting marigolds alongside tomatoes can deter nematodes, while planting garlic near roses can repel aphids.
- Nutrient enhancement: Some plants have the ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, making it more available to neighboring plants. For instance, planting legumes like beans or peas near nitrogen-demanding plants like corn or tomatoes can help provide them with the necessary nutrients.
- Space optimization: Companion planting can maximize space by combining plants with different growth habits. For example, tall plants like corn can provide shade for shorter plants like lettuce or spinach, allowing them to thrive in the same area.
By implementing companion planting techniques, gardeners can create a harmonious and productive garden ecosystem.
Use Raised Beds or Containers
Raised beds or containers can be used as an alternative gardening method that offers several advantages. One of the main benefits is the ability to maximize space in a garden. Raised beds, which are essentially elevated planting areas, allow for a more efficient use of space by eliminating the need for pathways between rows.
Additionally, they provide better control over soil conditions, as gardeners can customize the soil composition to suit the specific needs of their plants. Furthermore, raised beds and containers offer better drainage compared to traditional in-ground gardening, which can be especially beneficial in areas with heavy rainfall.
They also provide easier access for gardening tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting. Overall, raised beds or containers are an effective way to make the most of limited gardening space and can result in higher yields and healthier plants.
Choose the Right Plants
Selecting appropriate plant species is crucial for optimizing space in your garden, as it allows for the efficient utilization of resources and ensures maximum productivity. By choosing the right plants, you can make the most of limited garden space while still achieving a bountiful harvest.
Here are three key considerations when selecting plants for intensive gardening:
- Compact Growth: Look for plants that have a compact growth habit, such as bush varieties or dwarf cultivars. These plants take up less space and can be planted closer together, maximizing the use of available area.
- Vertical Gardening: Consider plants that can be trained to grow vertically, such as climbing beans, cucumbers, or tomatoes. Vertical gardening allows you to take advantage of vertical space, making use of trellises, stakes, or fences.
- Succession Planting: Choose plants that have a short growing season, enabling you to quickly replant the same space once one crop is harvested. This ensures continuous production throughout the growing season and maximizes the use of your garden space.
By carefully selecting the right plants, you can make the most of your garden’s limited space, increasing your overall yield and enjoying a productive and efficient garden.
Soil Preparation and Fertilization
This discussion will focus on key points related to soil preparation and fertilization.
The first key point is to improve soil quality with amendments, which involves adding substances such as compost, manure, or lime to enhance the soil’s fertility and structure.
Another important aspect is the use of organic fertilizers and compost, which provide essential nutrients to the plants in a natural and sustainable way.
Lastly, practicing crop rotation is crucial in order to prevent the depletion of nutrients from the soil and to minimize the risk of pest and disease buildup.
Improve Soil Quality with Amendments
To enhance the quality of soil, incorporating amendments is a crucial step in intensive gardening as it improves nutrient levels and boosts overall plant growth. Soil amendments are substances that are added to the soil to enhance its physical properties and fertility. Common amendments include compost, manure, peat moss, and vermiculite. These amendments improve soil structure by increasing its water-holding capacity, aeration, and drainage.
Additionally, they provide essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are necessary for plant growth. By incorporating amendments into the soil, gardeners can create a favorable environment for their plants to thrive. It is important to choose the right amendments based on the specific needs of the plants and the existing soil conditions. Regular soil testing can help determine the appropriate amendments to use for optimal results in intensive gardening.
Use Organic Fertilizers and Compost
Organic fertilizers and compost are essential for promoting healthy plant growth and creating a sustainable and environmentally friendly gardening practice. By incorporating these natural amendments into your garden, you can enrich the soil with essential nutrients, improve its structure, and enhance water retention capabilities.
Here are four key benefits of using organic fertilizers and compost:
- Nutrient-rich: Organic fertilizers and compost provide a wide range of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for plant growth.
- Soil health: These amendments improve the soil’s biological activity by promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms, earthworms, and other soil organisms.
- Environmental sustainability: Organic fertilizers and compost are derived from natural sources and do not contain harmful chemicals or synthetic substances that can harm the environment.
- Waste reduction: Composting organic materials diverts waste from landfills, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a circular economy.
By incorporating organic fertilizers and compost into your gardening practices, you can maximize the productivity of your garden while minimizing environmental impact.
Practice Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is a strategic agricultural practice that not only optimizes plant health and productivity but also fosters a sense of connection and harmony with the land.
It involves the systematic planting of different crops in successive years on the same piece of land.
The primary objective of crop rotation is to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases that are specific to certain plants. By changing the crop species grown in a given area, the life cycles of pests and diseases can be disrupted, reducing their impact on future crops.
Additionally, different crops have varying nutrient requirements, and crop rotation helps to maintain soil fertility by balancing nutrient uptake and minimizing depletion.
This practice also contributes to weed control, as certain crops can suppress or inhibit the growth of specific weeds.
Overall, crop rotation is an effective and sustainable method to maximize space and optimize plant health in intensive gardening.
Efficient Watering Techniques
Efficient watering techniques in intensive gardening involve utilizing drip irrigation systems and strategically placing mulch around plants to reduce evaporation and ensure optimal water distribution. Drip irrigation systems provide water directly to the roots of plants, minimizing water loss through evaporation and runoff. This method also helps prevent weed growth by watering only the plants and not the surrounding soil. Mulching, on the other hand, acts as a protective barrier that retains soil moisture and prevents weed growth. By covering the soil with a layer of organic materials such as straw, wood chips, or compost, evaporation is reduced, and the soil stays consistently moist. The table below illustrates the benefits and drawbacks of each technique.
| Technique | Benefits | Drawbacks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Efficient water distribution, reduced evaporation and runoff | Initial installation cost, requires maintenance | ||||
| Mulching | Soil moisture retention, weed prevention | Requires regular replenishment, possible termite risk | Rainwater harvesting | Conservation of water resources, reduced reliance on external sources | Requires proper storage and filtration systems | |
| Xeriscaping | Minimal water usage, promotes native plant growth | Initial investment in drought-tolerant plants and landscaping | ||||
| Soil amendment | Improves soil structure and nutrient content | Requires periodic application and monitoring | ||||
| Micro-sprinkler systems | Precise water application, customizable for different plant needs | Higher initial cost compared to traditional sprinklers | ||||
| Greywater recycling | Reuses household wastewater, reduces water waste | Requires separate plumbing system and regular maintenance | ||||
| Smart irrigation controllers | Automatic scheduling based on weather conditions, water-saving features | Requires initial setup and occasional adjustments | ||||
| Permeable paving | Allows water infiltration, reduces stormwater runoff | Requires proper maintenance to avoid clogging | ||||
| Drought-tolerant plants | Minimal water requirements, adaptable to arid conditions | May require initial investment in new plants | ||||
| Raised bed gardening | Improved soil drainage, easier weed management | Requires regular upkeep and soil amendments | ||||
| Terracing | Prevents soil erosion, maximizes water retention | Requires proper construction and occasional maintenance |
Pest and Disease Management
Efficient watering techniques are crucial for a successful garden, but another important aspect of gardening is pest and disease management. To maximize the productivity of an intensive garden, it is essential to address these challenges effectively.
Pest management involves identifying and controlling harmful insects, while disease management focuses on preventing and treating plant diseases. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a sustainable approach that combines various strategies such as biological control, cultural practices, and the use of pesticides as a last resort.
Additionally, crop rotation and companion planting can help deter pests and promote healthier plants. To achieve optimal results, gardeners should regularly monitor their plants, maintain proper sanitation, and implement preventive measures. By adopting these practices, gardeners can minimize the impact of pests and diseases, ensuring a bountiful harvest.
Strategies for Pest Management:
- Biological control
- Cultural practices
Techniques for Disease Management:
- Crop rotation
- Companion planting
Harvesting and Storage
Harvesting and storage is a critical aspect of maintaining the quality and longevity of garden produce. Proper harvesting techniques ensure that crops are picked at their peak ripeness, maximizing their flavor and nutritional value. It is essential to handle harvested produce with care to prevent bruising or damage that can lead to spoilage. Additionally, proper storage is vital to extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure must be considered when determining the best storage method for each type of crop. Storing produce in cool, dark, and well-ventilated areas can help prevent deterioration and preserve freshness. The table below provides examples of recommended storage methods for common garden crops:
| Crop | Storage Method |
|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Room temperature, out of direct sunlight |
| Carrots | In the refrigerator, in a perforated plastic bag |
| Apples | In the refrigerator, in a plastic bag |
| Potatoes | In a cool, dark, and dry place |
| Leafy greens | In the refrigerator, in a plastic bag or container with a damp paper towel |
By following proper harvesting and storage practices, gardeners can make the most of their produce and enjoy the fruits of their labor for an extended period.
Maintenance and Seasonal Care
Maintenance and seasonal care play an integral role in ensuring the health and longevity of garden crops, fostering a sense of fulfillment and joy in the hearts of dedicated gardeners. To maximize the potential of an intensive garden, attention must be given to regular maintenance tasks and seasonal adjustments.
Here are three key practices for effective garden care:
- Weed Control: Regular weeding is essential to prevent competition for nutrients, space, and sunlight. Mulching can help suppress weed growth and retain moisture, reducing the need for frequent weeding.
- Watering: Consistent and adequate watering is crucial, especially during dry spells. A drip irrigation system or soaker hoses can provide targeted watering, minimizing water waste and ensuring plants receive the necessary moisture.
- Pest and Disease Management: Regular monitoring and prompt action are needed to prevent pest infestations and disease outbreaks. Techniques like crop rotation, companion planting, and natural pest control methods can help minimize the need for chemical interventions.
By following these maintenance and seasonal care practices, gardeners can optimize their intensive gardens and enjoy bountiful harvests throughout the year.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common mistakes to avoid when practicing intensive gardening?
Common mistakes to avoid in intensive gardening include overcrowding plants, neglecting proper spacing, insufficient soil preparation, failure to rotate crops, inadequate pest management, and disregarding the need for appropriate watering and fertilization techniques.
Can I use raised beds for intensive gardening?
Raised beds are a suitable option for intensive gardening. They provide better soil drainage, prevent soil compaction, and allow for efficient space utilization. Additionally, raised beds facilitate easier weed control and reduce the risk of pests and diseases.
How can I prevent weeds from overtaking my intensive garden?
One way to prevent weeds from overtaking an intensive garden is by implementing mulching techniques such as using organic materials like straw, wood chips, or compost. Mulching helps to suppress weed growth by blocking sunlight and creating a barrier.
Is it possible to practice intensive gardening in a small balcony or patio?
Yes, it is possible to practice intensive gardening in a small balcony or patio. By utilizing vertical gardening techniques, container gardening, and careful plant selection, individuals can maximize their limited space for efficient and productive gardening.
Are there any specific tools or equipment that I need for intensive gardening?
Specific tools and equipment are required for intensive gardening. These may include raised beds, trellises, drip irrigation systems, hand tools such as trowels and pruners, and compost bins. These tools help optimize space and promote efficient gardening practices.